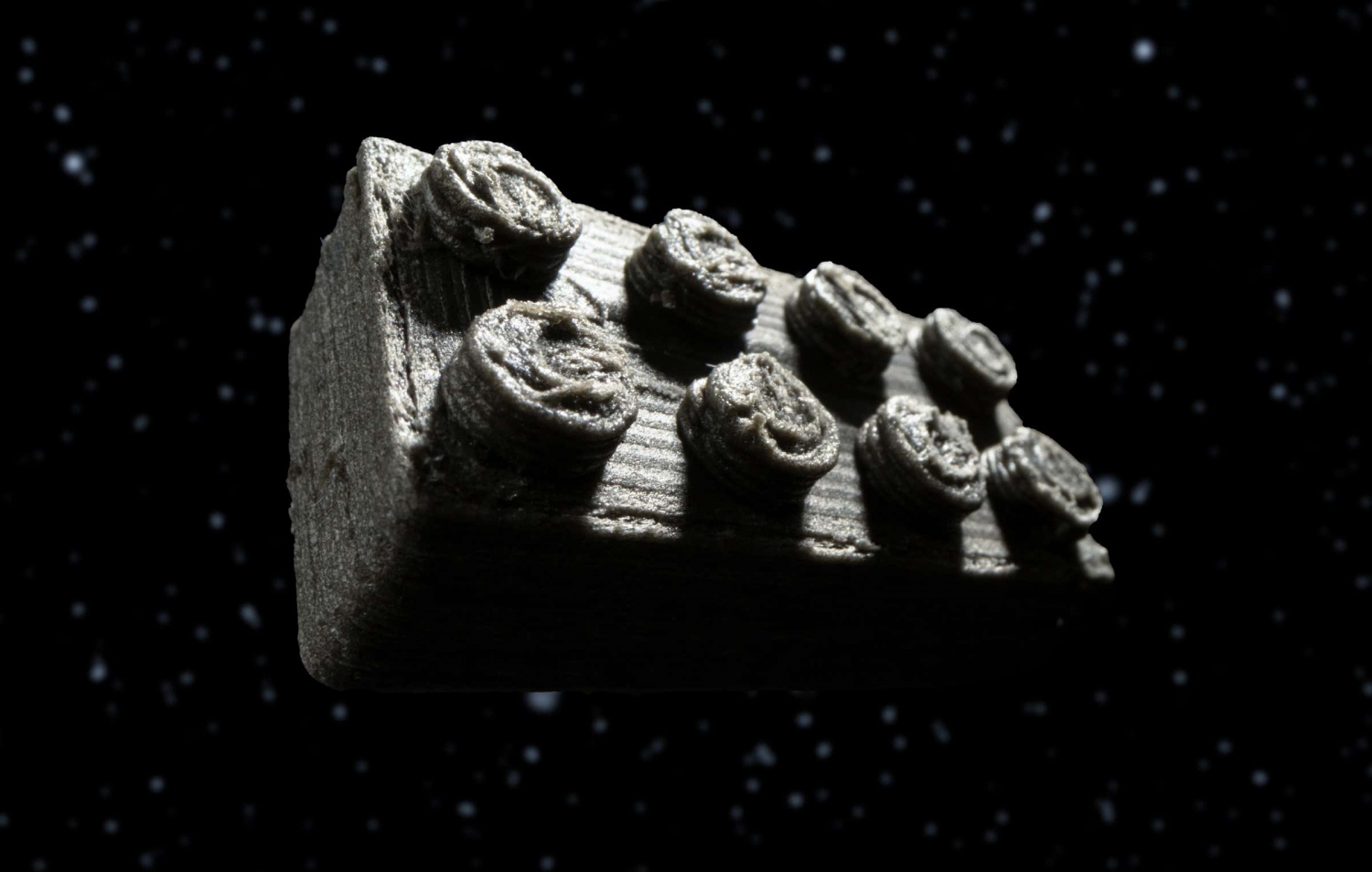
Scientists have used LEGO brick assembly techniques to design launch pads and shelters for Artemis program astronauts visiting the moon. Their pioneering approach involves using meteorite dust to 3D print LEGO-like bricks, evaluating their potential as fundamental components in scaled-down structures. scientists have pioneered a groundbreaking method for lunar exploration by utilizing 4.
5 billion-year-old meteorite dust to create 3D-printed LEGO-like bricks. Inspired by , these innovative bricks are designed to potentially serve as launch pads and shelters for astronauts in NASA's Artemis program. The ESA team's experiment involved 3D printing scaled-down structures using these bricks to test their feasibility and durability in extraterrestrial environments.

In partnership with , the ESA has been investigating various 3D printing techniques to evaluate their potential for fabricating components using indigenous materials sourced from the Moon or Mars. While stereolithography has proven effective for producing small-scale components and large-format construction has been applied to building structures. The production of bricks using extraterrestrial resources represents a pioneering leap forward in space construction technology.
While creating bricks from a blend of dust and a polymer matrix may not seem revolutionary, the forthcoming tests on these bricks aim to yield crucial insights into their resilience and endurance under the harsh conditions of outer space. Initially, th.